The optic disc margin defined by high-speed ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography was significantly different from the margin defined by disc photography in a study of 17 healthy volunteers at the
From May through November 2005, the subjects (17 eyes) had raster scans centered on the optic disc taken with stereo-optic disc photography and high-speed ultrahigh-resolution OCT (hsUHR-OCT). Two image outputs were derived from the hsUHR-OCT data set: an en face hsUHR-OCT fundus image and a set of 180 frames of cross-sectional images. Three ophthalmologists independently and in a masked, randomized fashion marked the disc margin on the disc photography, hsUHR-OCT fundus and cross-sectional images using custom software. Disc size (area and horizontal and vertical diameters) and location of the geometric disc center were compared among the three types of images.
The hsUHR-OCT fundus image definition showed a significantly smaller disc size than the disc photography definition (p<.001, mixed-effects analysis). The hsUHR-OCT cross-sectional image definition showed a significantly larger disc size than the DP definition (p<.001). The geometric disc center location was similar among the three types of images except for the y-coordinate, which was significantly smaller in the hsUHR-OCT fundus images than in the disc photography images.
(Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126:58-64.)
Manassakorn A, Ishikawa H, Kim JS, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Kagemann L, Gabriele ML, Sung KR, Mumcuoglu T, Duker JS, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS.
25-Gauge PPV Infection Rates Higher than 20-Gauge
A retrospective study at several
The researchers compared the rates of endophthalmitis during a two-year study period and investigated clinical features of and visual acuity outcomes for patients with endophthalmitis after PPV. The incidence of endophthalmitis was two cases per 6,375 patients (or one case per 3,188 patients; 0.03 percent) for 20-ga. PPV compared with 11 cases per 1,307 patients (or one case per 119 patients; 0.84 percent) for 25-ga. PPV (p< 0.0001). Of 11 eyes that developed endophthalmitis after 25-ga. PPV, nine received endophthalmitis prophylaxis with subconjunctival cefazolin after surgery.
Median intraocular pressure on postoperative day one was 13 mmHg (range, 5 to 27 mmHg). Median time between PPV and endophthalmitis presentation was three days (range, 1 to 15 days). Presenting vision was hand motions or better in all eyes. Initial treatment included vitreous tap and injection of antibiotics in nine eyes and PPV and injection of antibiotics in two.
All patients received intraocular treatment with vancomycin, and 10 received ceftazidime treatment. Eight patients had final visual acuity of ≥20/400, and four had visual acuity of ≥20/63. Cultures were negative in three cases; no culture specimens were obtained in one case. Six of the seven isolates were coagulase-negative staphylococci, and one was enterococcus. Five of six isolates tested for sensitivity to vancomycin were sensitive, and both isolates tested for sensitivity to ceftazidime were sensitive.
(Retina 2008;28:138-142.)
Scott IU, Flynn HWJr., Dev S, Shaikh S, Mittra RA, Arevalo JF, Kychenthal A, Acar N.
Personality Type of the Glaucoma Patient
Noting that the psychologic aspects of glaucoma have been commented upon as early as 1818 by one observer who noted the excitable temperament of glaucoma patients, research centered at the
They evaluated 56 open-angle glaucoma and 52 controls with the MMPI-2 test and automated perimetry, and collected clinical and demographic information which could relate to personality type.
OAG subjects had significantly higher hypochondriasis (Hs; p= 0.0082), hysteria (Hy; p=0.0056), and health concerns (HEA; p=0.0025) mean scores than the control group. OAG subjects also had a significantly greater frequency of clinically abnormal score for hysteria (p=0.0262), and health concerns (p=0.0018). Multivariate analysis of variance revealed that all three scores were related to number of systemic medications used and to diagnostic group. Other potential explanatory variables such as sex, ethnicity, number of medical problems, length of glaucoma diagnosis, occurrence of glaucoma surgery, intraocular pressure and visual status were not related to these personality scores.
Patients with a diagnosis of OAG had more abnormal MMPI-2 scores in areas that focus upon concerns of somatic complaints and poor health. The use of systemic medications, which may be a constant reminder of illness, is a factor that may contribute to higher MMPI-2 scores.
(J Glaucoma 2007;16:649-654.)
Lim MC,
Cyclosporine Affects Cells in Ways that Tears Cannot
Cyclosporine emulsion increases goblet cell density and production of the immunoregulatory factor TGF-‚2 in the bulbar conjunctiva in patients with dry eye, while artificial tears do not, says an Allergan-supported study at the Ocular Surface Center, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. A group there evaluated the effects of sequential treatment with artificial tears and cyclosporine emulsion on conjunctival goblet cell density and production of transforming growth factor (TGF)2 in patients with dry-eye disease.
Six patients with dry-eye disease defined by an Ocular Surface Disease Index symptom score ≥25, Schirmer test 1 <10 mm, and corneal fluorescein and conjunctival lissamine green staining scores ≥3 were treated with artificial tears (Refresh Plus, Allergan) four times a day for four weeks, followed by 0.05% cyclosporine emulsion (Restasis, Allergan) twice a day for 12 weeks. Impression cytology was performed on the bulbar conjunctiva of both eyes at baseline, after artificial tear therapy, and after six and 12 weeks of cyclosporine therapy. Goblet cells were counted in five representative microscopic fields per membrane in those taken from the temporal and inferior bulbar conjunctiva of the worse eye, and membranes taken from the fellow eye were immunostained for TGF-B2.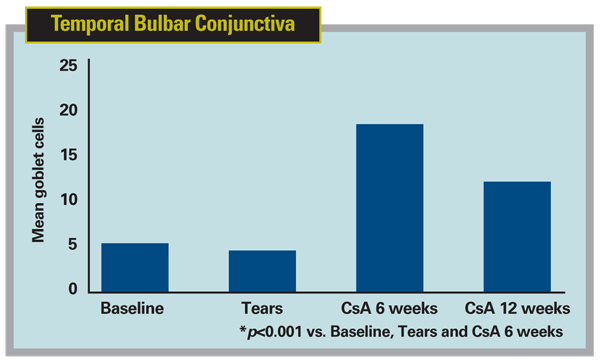
There were no differences in mean goblet cell density between baseline and four weeks of artificial tears in the temporal and inferior bulbar specimens. After six weeks of cyclosporine emulsion, goblet cell density was significantly greater than baseline and artificial tears in the inferior bulbar conjunctiva (p< 0.01). After 12 weeks of cyclosporine emulsion, goblet cell density was significantly greater than baseline and artificial tears in both temporal and inferior bulbar sites (p< 0.01). The number of TGF-‚2-positive goblet cells was also noted to increase after six and 12 weeks of cyclosporine therapy (p< 0.001).
(Cornea 2008;27;64-69.)
Pflugfelder S, De Paiva C, Villarreal A, Stern M.




