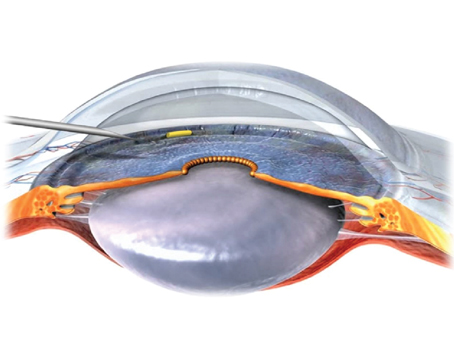
While flanged iris hooks have been used off-label for capsular bag stabilization and IOL centration in complicated cases of cataract surgery in previous reports, scientists wrote of a lack of data on the optimal flange technique of iris hooks made from different materials. They aimed to assess the flange properties of different iris hooks, as part of a masked laboratory study.
The flanging properties of four different iris hooks made from polypropylene, elastic polymer and nylon were investigated with different heating distances and both with and without forceps gripping. The maximum diameter of the flanges was measured, and the shape of the flanges was evaluated.
While the flange diameters of both nylon and elastic polymer iris hooks were too-small flange diameters for intrascleral fixation, polypropylene iris hooks had a sufficient flange diameter (>330 µm) and mushroom-like shape. Furthermore, in polypropylene hooks, heating distance was directly proportional to flange diameter.
Scientists wrote that the findings suggested that only polypropylene iris hooks were suitable for flanged intrascleral fixation, which is off-label, to secure adequate fixation.
J Cataract Refract Surg 2023; Nov 23. [Epub ahead of print].
Schlatter A, Kronschläger M, Ruiss M, et al.
Days of the Week and IOP
Researchers in Japan analyzed intraocular pressure by day of the week using a “mega database” to reveal weekly patterns. They evaluated annual health checkup examinees between April 2014 and March 2015. A total of 655,818 participants (51.5 ±10.5 [range, 20 to 96] years; 40.1 percent women]) from 103 medical centers were included.
IOP was measured using a non-contact tonometer. Mean IOPs of each day of the week were compared using multiple comparison tests and multiple linear regression analysis. Wednesday was set as the reference. Weekly IOP variations stratified by sex and age were also evaluated.
Here are some of the findings:
• Mean IOPs from Monday to Sunday were: 13.19 ±2.97, 13.06 ±2.92, 13.05 ±2.91, 13.05 ±2.92, 13.12 ±2.94, 13.10 ±2.96 and 13.16±2.78 mmHg.
• IOPs were significantly higher on Monday, Friday and Saturday than those on Wednesday (p<0.001; p<0.001; and p=0.002).
• After adjusting for factors affecting IOP, IOPs on Monday and Saturday (β=0.097; CI. 0.074 to 0.121; p<0.001) were higher than those on Wednesday (β=0.032; CI, 0.005 to 0.059; p=0.019).
• Men had significantly higher IOPs on Monday and Saturday than on Wednesday (β=0.142; CI, 0.110 to 0.173; p<0.001; β=0.053; CI, 0.017 to 0.089; p=0.004), although women didn’t have a significant trend.
• Participants ages <65 years had higher IOPs on Monday (p<0.001 for under 60 years; p=0.003 for 60 to 64 years) while those ages ≥65 years didn’t (p=0.856).
Researchers wrote that IOP values may have a periodic weekly pattern with high IOPs on Monday more pronounced in men ages <65 years.
J Glaucoma. 2023 Nov 3. [Epub ahead of print].
Terauchi R, Wada T, Fukai K, et al.
Postural Blood Pressure’s Association with POAG
 |
| Researchers say that assessing patients’ blood-pressure response to lying down vs. sitting may be a simple way to evaluate their risk for primary open-angle glaucoma. |
Researchers evaluated whether primary open-angle glaucoma patients demonstrated abnormal postural blood pressure response to recumbency and whether such a response correlated with glaucoma severity.
This prospective observational study included 47 POAG patients who underwent intraocular pressure; and systemic arterial (SABP), systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure measurements in seated positions and after twenty-minute recumbency positions. Mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) was calculated for seated and recumbent positions. The percentage difference between seated and recumbent SBP, DBP and MABP was calculated according to which participants were divided into three groups:
• non-dippers (percentage dips of <10 percent);
• normal dippers (percentage dips of ≥10 percent ≤20 percent); and
• exaggerated dippers (percentage dips of >20 percent).
Participants underwent optical coherence tomography of optic nerve head to measure retinal nerve fiber layer thickness, which was used as a structural biomarker of glaucoma.
Here are some of the findings:
• RNFL thickness was lower in exaggerated dippers than non-dippers and normal dippers.
• A negative correlation was found between postural dip and average RNFL thickness.
• Linear regression showed that postural dip was associated with lower RNFL thickness independent of age and IOP.
• Chi-square independence tests demonstrated a strong relationship between corresponding dip groups for SBP, DBP and MABP. However, it showed no significant relation between hypertension and postural dip.
• Fisher’s exact test showed no relation between anti-hypertensive medication and postural dips.
POAG patients demonstrated abnormal postural blood pressure response and exaggerated recumbent dips, which was positively correlated with disease severity. Researchers wrote that postural dip assessments may serve as a simple clinic-based test of systemic vascular dysregulation as part of glaucoma risk evaluation.
J Glaucoma 2023; Nov 28. [Epub ahead of print].
Ameen Ismail A, Sadek SH, Kamal MA, et al.
Utility of Widefield OCTA for Detecting RNV in PDR
Investigators assessed the real-world clinical utility of widefield OCTA for detecting retinal neovascularization in eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy, as part of a retrospective cross-sectional study.
They looked at consecutive eyes clinically suspected of PDR by physicians at a tertiary eye center between March 2021 and November 2022.
All eyes underwent ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography (Optos California) and widefield OCTA (Canon S1) with a 23 × 20 mm scan area. Two independent graders detected individual RNV lesions using UWF-FA and used them as the ground truth. Widefield OCTA images were first evaluated to determine whether the images successfully illustrated retinal vasculature, regardless of the image quality index or the presence of vitreous hemorrhage. The graders then identified the RNV lesions with widefield OCTA. Investigators detected RNV by utilizing the whole retinal slab, including flow signals in the retina, and the custom vitreoretinal interface slab, defined as flow signals from 20 microns below the internal limiting membrane to 2,000 µm above the ILM. They evaluated the applicability to real-world clinical practice by not correcting segmentation errors.
Main outcome measures included the success rate of imaging and the detection rate of RNV using WF-OCTA.
Sixty-nine consecutive patients who underwent UWF-FA were identified. Of these, 114 eyes from 57 (83 percent) patients underwent both UWF-FA and widefield OCTA. Of the 114 eyes, 108 (95 percent) produced gradable widefield OCTA images. Here are some of the findings:
• Using UWF-FA, the graders identified 175 RNV lesions in 40 eyes.
• Widefield OCTA had a sensitivity of 95 percent and specificity of 88 percent for detecting eyes with RNV.
• At the level of individual RNV lesions, graders detected 156 RNV lesions with widefield OCTA, with 118 of these confirmed by UWF-FA (true positive).
• Among the 57 false negative lesions, the primary causes were being out of the scan range (26 lesions) and segmentation errors (21 lesions).
Investigators reported that widefield OCTA imaging had a high success rate for detecting eyes with retinal neovascularization in a real-world clinical setting. Despite a 67 percent detection rate for individual retinal neovascularization lesions, they suggested that the imaging modality may serve as a valuable noninvasive method for detecting retinal neovascularization detection in eyes with diabetic retinopathy.
Ophthalmol Retina 2023; Nov 24. [Epub ahead of print].
Hamada M, Hirai K, Wakabayashi T, et al.
Optic Disc Drusen in RP
Researchers wrote that studies of patients with retinitis pigmentosa have reported an increased prevalence of optic disc drusen (ODD) compared with ODD prevalence in the general population. They added that the diagnostic gold standard method for identifying ODD is enhanced-depth imaging optical coherence tomography (EDI-OCT) but that the modality hasn’t previously been used systematically for identifying ODD in patients with RP. This study aimed to estimate the prevalence of ODD in patients with RP using EDI-OCT.
In this cross-sectional study, 40 patients with clinically diagnosed RP, ages 18 or older were included. All patients underwent an ophthalmic exam, including kinetic perimetry, EDI-OCT of the optic nerve head and fundus photography. Genetic testing with a next-generation sequencing panel of retinal dystrophy genes was performed on the RP patients without a prior genetic diagnosis. Here are some of the findings:
• Twelve patients (30 percent) had at least one ODD.
• Six patients had bilateral ODD.
• No significant differences between patients with and without ODD were found according to age, refraction, best-corrected visual acuity, Bruch’s membrane opening or visual field.
• The genetic variation causing RP was found in 11 of 12 cases in the ODD group, and in 17 of 28 cases in the group without ODD.
Researchers say the prevalence of ODD in patients with RP was 15 times higher than in the general population and much higher than previously estimated, potentially indicating that the two conditions might be pathogenically related.
J Neuroophthalmol 2023; Nov 17. [Epub ahead of print].
Steensberg AH, Schmidt DC, Malmqvist L, et al.
Angle Kappa and Power Calcs
Scientists evaluated the effect of ocular biomechanics on the prediction error of IOL power calculation in an ophthalmology department at Centro Hospitalar Universitário do Porto in Portugal, as part of a prospective longitudinal study.
Before cataract surgery, the subjects underwent biometry with IOL Master 700 (Zeiss) and biomechanical analysis with Corvis Scheimpflug Technology (Oculus). The targeted spherical equivalent was calculated with SRK-T and Barrett Universal II.
This study included 67 subjects. Here are some of the findings:
• Using the SRKT formula, an association was found between:
– PE and Corvis Biomechanical Index (CBI, B=-0.531; p=0.011); and
– AE and the horizontal offset between the center of the pupil and the visual axis (angle kappa, B=-0.274; p=0.007).
• Using the Barrett Universal II formula:
– PE was independently associated with anterior chamber depth (B=-0.279; p=0.021); and
– CBI (B=-0.520; p=0.013) and AE were associated with angle kappa (B=-0.370, p=0.007).
Scientists concluded that a large angle kappa may reduce the predictability of IOL power calculation and that ocular biomechanics likely influence the refractive outcomes after IOL implantation. They added that eyes with softer corneal biomechanics had more myopic prediction error, which may relate to anteriorization of the effective lens position, and suggested that dynamic measurements may pave the way for future formulas.
J Cataract Refract Surg 2023; Nov 13. [Epub ahead of print].
Marques JH, Baptista PM, Ribeiro B, et al.
OCT/OCTA for Tracking Glaucoma Progression
Researchers examined event-based glaucoma progression using optical coherence tomography and OCT angiography, as part of a retrospective study.
Glaucoma eyes with ≥two- and four-visits with OCT/OCTA imaging were included. Peripapillary capillary density (CD) and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness were obtained from 4.5 × 4.5 mm optic nerve head scans. Event-based OCT/OCTA progression was defined as decreases in ONH measurements exceeding test-retest variability on ≥two consecutive visits. Visual field progression was defined as significant VF mean deviation worsening rates on ≥two consecutive visits.
Here are some of the findings:
• Among 147 eyes (89 participants), OCTA identified 33 progressors (22 percent) and OCT identified 25 progressors (17 percent).
• They showed slight agreement (κ=0.06), with 7 eyes (5 percent) categorized as progressors by both.
• When incorporating both instruments, the rate of progressors identified increased to 34 percent.
• Similar agreement was observed in diagnosis- and severity-stratified analyses (κ<0.10).
• Compared to progressors identified only by OCT, progressors identified only by OCTA tended to have thinner baseline RNFL and worse baseline VF.
• VF progression was identified in 11 eyes (7 percent).
• OCT and VF showed fair agreement (κ=0.26), with six eyes (4 percent) categorized as progressors by both.
• OCTA and VF showed slight agreement (κ=0.08), with four eyes (3 percent) categorized as progressors by both.
Researchers found that OCT and OCTA showed limited agreement on event-based progression detection, with OCT showing better agreement with visual field. Researchers concluded that OCT and OCTA may provide valuable, yet different and complementary, information about glaucoma progression.
Eye (Lond) 2023; Nov 11. [Epub ahead of print].
Wu JH, Moghimi S, Nishida T, et al.