This year's ARVO meeting in- cludes a number of presentations on refractive topics, ranging from flap-making comparisons to examinations of dark-adapted pupil size. There are also investigations into ectasia and how different procedures may weaken the cornea. For an executive summary of these papers to help you decide which might be useful in your practice, read on.
(Researchers have no financial interest in the subject matter of their abstracts, unless otherwise noted.)
Making Flaps
Surgeons from the Mayo Clinic in
In the prospective study, the researchers performed bilateral LASIK on the eyes of 21 patients. One eye of each patient was randomized to flap creation with the femtosecond laser with an intended thickness of 120 µm, with the fellow eye undergoing flap creation with the keratome with an intended thickness of 180 µm.
They examined the corneas with confocal microscopy up to 12 months postop. The researchers determined epithelial thickness from the number of video frames between images of the epithelial surface and subbasal nerve plexus and determined flap thickness by the number of frames between images of the epithelial surface and interface particles.
The researchers say the epithelial thickness didn't differ between the treatment groups at any time; the mean minimum detectable difference was 9.3 µm. The postop epithelial thickness didn't differ from preop at any time point, with a mean minimum detectable difference of 7.3 µm. The measured flap thickness differed from the intended for both (p
≤ 0.001).5329
PRK and LASIK Findings
After following patients for as long as seven years, surgeons from the Stanford University School of Medicine say that the Visx laser is effective and safe for treating hyperopia of up to +6 D. One of the surgeons received financial support from Visx and AMO.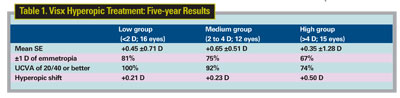
The researchers prospectively analyzed 43 eyes of 26 consecutive patients. The patients were divided into three groups based on preop cycloplegic refraction: low (<2 D; 16 eyes); medium (2 to 4 D; 12 eyes); and high (>4 D; 15 eyes). The average preop SE was +2.7 D (range: +0.75 to +6 D) and the attempted average spherical correction was +2.76 D (range: +0.75 to +5.75 D). The average follow-up was five years (range: three to seven years). The surgeons say the procedure has been predictable, and that regression has been acceptable after five years (+0.32 D overall; range: -1.25 to +2.63 D). (The five-year results appear above).1985
Surgeons from the Federal University of Sao Paulo in
In this prospective study, 88 eyes of 44 patients with a minimum estimated ablation depth of 50 µm were randomized to custom PRK with MMC 0.002% for one minute in one eye and custom LASIK in the fellow. The mean preop SE before surgery was -3.99 ±1.2 D for the LASIK eyes and -3.85 ±1.12 D for the PRK eyes. The average ablation depth was 73.09 ±14.6 µm for LASIK and 70.7 ±14.07 µm for PRK.
At six months, the mean uncorrected acuities were -0.10 ±0.09 in LASIK eyes and -0.13 ±0.10 in PRK eyes (p>0.05). The average cycloplegic SE error in the LASIK group was 0.52 ±0.56 D, while the average in the PRK group was 0.56 ±0.34 D. There was no significant haze in any PRK eye. The average higher-order aberrations were higher in the LASIK eyes (p<0.04), and the PRK eyes showed better contrast sensitivity than the LASIK eyes. In terms of visual satisfaction, patients rated the PRK eyes better than their LASIK eyes. The researchers say longer follow-up will be necessary to confirm long-term safety of MMC with PRK.1992
Air Force surgeons at the
Retrospectively, the researchers compared 226 custom treatments performed with the Alcon LADARVision platform to 226 done with the Visx CustomVue system over an 18-month period. They matched eyes based on age, preop manifest SE and cylinder.
The surgeons found that patients treated on the LADARVision system were significantly closer to plano at one month, with an average postop manifest SE of -0.08 D at that time, compared to -0.29 D at one month on the Visx system. However, by three months, the LADARVision patients had an average postop manifest SE that was slightly hyperopic (+0.11 D at three months, +0.10 D at six and +0.05 D at a year). At the same time points, patients treated with the Visx system retained an average postop manifest SE that was slightly myopic (-0.06 D at three months, -0.04 D at six months and -0.04 D at a year). Subgroup analysis also showed that LASEK ablations with the LADARVision platform had significantly better uncorrected vision than those done with the Visx at one month (20/20.7 vs. 20/28.6); by three months the difference was no longer present.5357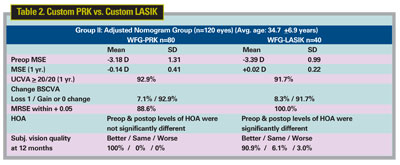
Surgeons from
Eighty-eight cases of low hyperopia (up to +4 D) with or without astigmatism were divided between the two lasers for treatment and retrospectively evaluated. In the Allegretto group, the mean preop refraction was 2.35 D for sphere and 0.04 D for cylinder, compared to 2.02 D sphere and 0.68 D cylinder for the Visx. Postop, of the eyes in the Allegretto group, 79.5 percent were within ±0.50 D of the refractive goal and 47.7 percent had vision 20/20 or better. For the Visx group, 95.4 percent were within ±0.50 D of intended, and 59 percent saw 20/20 or better. The surgeons say there was no difference in the two groups in relation to the patients achieving 20/20 uncorrected (p=0.20). However, there was a statistically significant difference when the postop refraction under +0.50 D was considered (p<0.001).2365
Surgeons at Walter Reed Army Medical Center in Washington and the Naval Medical Centers in San Diego and Washington have completed a one-year, prospective study of conventional and wavefront-guided PRK and LASIK.
In the study, a total of 135 subjects received either standard PRK (50 eyes), standard LASIK (25 eyes), custom PRK (130 eyes) or custom LASIK (65 eyes). Seventy-five patients serving as a nomogram adjustment group had a custom treatment in one eye and a standard treatment in the fellow eye (50 PRK and 25 LASIK). The final 60 subjects were treated with bilateral custom PRK (40 patients) or custom LASIK (20 patients) using an adjusted nomogram. The surgeons used the Alcon LADARVision 4000 excimer laser for all the procedures. Interestingly, the nomogram-adjusted custom PRK and LASIK didn't perform better than the standard groups, though both groups had excellent results. The custom results appear in Table 2 above.5346
A group of surgeons from
The surgeons retrospectively analyzed 23 eyes of PK patients who received MMC during their PRK procedures. The MMC protocol was 0.02% MMC for 30 seconds. The preop SE was -5.24 ±3.32 D and best-corrected vision was 0.68 ±0.12 (~20/32).
Postop, at 12 months (range: nine to 18), the SE was -1.15 ±0.92 D, and best-corrected vision was 0.72 ±0.14 (~20/30). Seventy-two percent of the eyes saw 20/40 uncorrected, and 36 percent saw 20/25 or better. There were no side effects, haze or toxic effects.5364
Postop Problems
Researchers from the
In this prospective study, surgeons tested the ability of 41 patients to detect and identify two different road signs and a pedestrian hazard during simulated night driving on a rural road at 55 mph, with and without glare. The testing was conducted before and six months after custom LASIK (n=21) and PRK (n=20) with a Visx laser. The preop SE was -4.96 ±0.63 D (the treatment groups were designed to be similar along the lines of sphere and cylinder). Each eye was tested independently. All of the subjects were tested in their spectacles. Another group of 44 patients (88 eyes) who had received conventional LASIK were used for comparison.
The researchers say they found significant differences between the custom and conventional groups (p<0.01), with the custom group's average improvement in recognition time being 310 msec, while conventional patients averaged a loss of 350 msec. Contrast sensitivity, the extent of preop myopia and residual refractive error all correlated with the change in visual performance during simulated night driving.1989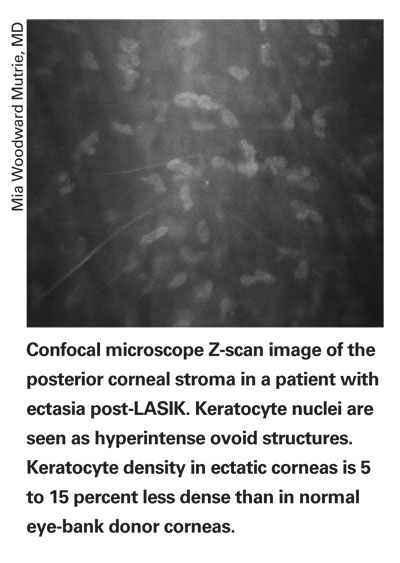
Researchers at
The physicians used timolol b.i.d. in 32 eyes of 19 patients who had myopic regression and decreased acuity (spherical equivalent of -1 D or greater) after LASIK. The patients' average preop SE was -9.6 D in the right eye and -9.9 D in the left. They began the regimen two to 36 months after the surgeries when a residual myopia of -1.87 D was noted, and the patients were followed for up to 38 months.
After 1.78 months the SE was reduced to -0.94 ±0.57 D (range: 0 to -1.75 D; p<0.0001). Uncorrected acuity improved from 0.34 ±0.15 (~20/63) to 0.63 ±0.23 (~20/32) (p<0.0001). Intraocular pressure didn't change. Patients who continued to use the timolol maintained a lower SE at the last follow-up visit compared to those who discontinued the treatment (-1 ±0.43 D vs. -1.59 ±0.66 D; p=0.025). The interval between the surgery and the start of the timolol treatment didn't affect the SE effect.5334
Surgeons from Bascom Palmer examined post-LASIK ectasia corneal buttons and normal corneas to get a feel for how much refractive surgery weakens the cornea.
The physicians used light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy to evaluate the histology and ultrastructure of six post-LASIK ectasia buttons. They also measured the cohesive tensile strength of five normal eye bank donors in the anterior third of the corneal stroma and compared this to measurements taken in the mid and posterior thirds of the corneal stroma.
All post-LASIK ectasia corneal buttons had the thinnest residual stromal bed thicknesses (less than 300 µm) and all buttons had at least one full-thickness Bowman's layer break over the region of ectasia. Ultrastructurally, all buttons had thinner corneal lamellae (less than 1 µm compared to the normal 2 to 3 µm) in the ectatic region of the residual stromal bed. The keratocyte density in the ectatic region of each button was not significantly different from normal post-LASIK corneas, but overall was 5 to 15 percent less dense than normal eye bank donor corneas.
In normal corneal buttons, the corneal stromal tensile strength was highest in Bowman's layer (50 g/mm) and the peripheral anterior third (40 g/mm) followed by the central anterior third (35 g/mm) and peripheral posterior two-thirds (30 g/mm) of the corneal stroma. The weakest region of the corneal stroma was the central posterior two-thirds (20 g/mm).
The researchers say that, similar to keratoconus, early stages of ectasia can be observed on light microscopy at Bowman's layer, but it is markedly less severe in degree.
In general, they say their corneal physiology studies show that the central anterior third of the corneal stroma supports 45 percent of the eye-wall stress, and that LASIK surgery approximations suggest an average reduced central tensile strength of 27 percent. They say that advanced surface ablation reduces the tensile strength by an average of 13 percent.3513
Researchers from
The study was a retrospective chart review. The researchers measured Corneal Hysteresis (CH) and Corneal Resistance Factor (CRF) in the patients' eyes. They compared the signals from the ORA, including Goldmann-equivalent IOP, corneal-compensated IOP, CH and CRF values. The ORA measures IOP with the cornea in motion at inward applanation (P1) and outward applanation (P2). The formula CH = P1 - P2 represents viscous damping of the cornea while CRF = P1 - (0.70 x P2) represents the total corneal viscoelastic response to deformation.
Normal eyes (n=202) had a CH of 10.28 ±1.39 mmHg, and a CRF of 10.76 ±1.25 mmHg. Keratoconus eyes (n=76) had a CH of 8.30 ±2.35 mmHg and a CRF of 7.15 ±2.41 mmHg. The researchers say the differences in CH (-2.47 mm Hg) and CRF (-3.13 mm Hg) between normal and keratoconus eyes were both very significant (p<0.001). The waveform of ORA signals of keratoconus eyes were short in amplitude and had multiphasic waves as compared to the smooth and high uniphasic waves of the normal cornea.
Pre-LASIK eyes (n=98) had a CH of 10.46 ±1.71 mmHg, and a CRF of 10.25 ±1.88 mmHg. Post-LASIK eyes (n=98) had a CH of 8.63 ±1.72 mmHg and a CRF of 7.28 ±1.82 mmHg. The differences in CH (-1.84 mm Hg) and CRF (-2.97 mm Hg) between these two groups were very significant (p<0.001). Most post-LASIK eyes have smooth uniphasic waveforms, however.2361
Miscellaneous Reports
Surgeons from the
The surgeons implanted a Staar Visian ICL in 49 eyes of 29 patients with moderate to high myopia, with an average follow-up of 21 months. They prospectively evaluated the trabecular-iris angle (TIA); angle opening distance (AOD), or the distance between the trabecular meshwork and the iris; and the AOD measured at 500 µm from the scleral spur, which they called the AOD-500. They also evaluated the eyes' trabecular pigmentation preoperatively and early (one to three months), mid (six to 12 months), and late (more than 18 months) postop, using ultrasound and gonioscopy.
The surgeons say TIA and AOD-500 decreased significantly from preop to early postop periods (p<0.001), but no significantly progressive changes occurred afterward. In at least one quadrant, trabecular pigmentation increased in 41.7 percent of patients from the preop to early-postop periods and in 16.7 percent from the early- to late-postoperative periods. Uncorrected vision and best-corrected vision improved significantly after surgery (p<0.001), and 83.3 percent of patients were within 0.5 D and 94.4 percent were within 1 D of the intended refraction.
The surgeons say IOP remained stable in all eyes after surgery except in one eye, which showed increased IOP and consistently increased trabecular pigmentation. The physicians needed to use anti-glaucoma medications to keep the pressure normal. Corneal endothelial cell density decreased significantly from preoperative to early-postoperative periods (p=0.026), but the researchers didn't detect any ongoing chronic loss of corneal endothelial cells while following the patients. 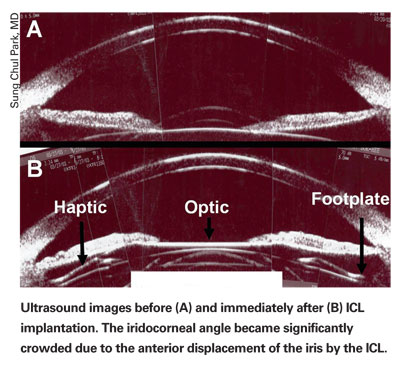
Because of their findings, the surgeons recommend close follow-up of ICL patients, with careful monitoring of iridocorneal angle status and IOP.1996
Surgeons from
The researchers used the Visx WaveScan to examine 28 eyes of 15 healthy volunteers. First, they captured a set of three scans in a room with minimal ambient illumination, then performed a standard dark-adaptation protocol. They then captured two additional sets of three scans each at five and 15 minutes of dark adaptation. They took the largest pupil diameter of the three scans at each interval.
Subjects averaged 28.5 years of age, with an average SE error of -3.62 D. The average pupil diameter at baseline (zero min.) was 7.74 mm. At five minutes, the average diameter was 7.45 mm, and at 15 minutes it was 7.37 mm. The physicians say that, though the five-minute size wasn't statistically significantly different than baseline, they were surprised to find that the 15-minute pupils were (p<0.005). They say that the results suggest that ablation zone sizes in refractive surgery may be made smaller in comparison to those values obtained with current scotopic pupil measurement techniques. They add that the smaller dark-adapted pupil size at 15 minutes may also have implications for increasing the number of refractive surgery candidates and reducing the reported incidence of night-vision disturbances.2363
Dr. Probst is the Chicago-land regional medical director for TLC Laser Centers.