During the past year, researchers around the world have continued to make progress in glaucoma-related areas, ranging from visual evoked potential instrumentation to surgical techniques. Here are selected abstracts from this year's program.
Prostaglandins
Treatment impact on contralateral eye. A retrospective review of charts conducted at Hines Veterans Administration Hospital in Chicago found that patients who responded successfully to treatment in one eye with travoprost (Travatan, Alcon) (n=22) or bimatoprost (Lumigan, Allergan) (n=17) also showed a statistically significant decrease in IOP in the contralateral eye. Travoprost reduced IOP 33.3 percent in the treated eye and 7.1 percent in the contralateral eye; bimatoprost caused a 35.3-percent drop in the treated eye and an 11.3-percent drop in the other eye.3767
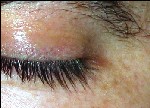
Preventing cosmetic side effects. A prospective, randomized, single-masked, internally controlled clinical study at the University of Rome demonstrated that the hypertricosis and periocular skin pigmentation that often accompanies bimatoprost topical therapy can be minimized by wiping the eye with an absorbent pad after administering the drop. Ten subjects not previously treated with prostaglandins received bimatoprost in both eyes. One eye was wiped for the first three months; both eyes were wiped for the second three months. Two independent masked investigators then assessed high-resolution digital photographs of the patients.
By the third month, the unwiped eyes had significantly longer eyelashes (29 percent growth vs. 19 percent). At month six, after three months of wiping both eyes, the eye that was only wiped for the second three months showed a trend of growth reversal (-5.6 percent) while the other eye remained stable (+0.5 percent). Hypertricosis and skin pigmentation appeared to show a similar reversal trend.2457
|
|
 |
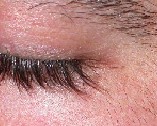 |
| Hair growth and skin pigmentation that often accompanies bimatoprost topical therapy can be minimized by wiping the eye with an absorbent pad after administering the drop. The eye above received treatment without post-drop wiping for three months, followed by three months with post-drop wiping. During the second three months, lash growth reversed and skin pigmentation improved. |
Asymmetry in IOP measurements. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, evaluated interocular pressure asymmetry over a 24-hour period in 53 healthy older patients and 41 glaucomatous older patients. Subjects' IOPs were measured every two hours for 24 hours, both sitting and supine during waking hours, and in the supine position at night.
Researchers found that the mean IOP in the right eye of healthy subjects was consistently higher than mean IOP in the left eye—a significant difference (18.3 ±2.1 vs. 17.9 ±2.2 mmHg). However, no significant difference between left and right IOP was found in glaucoma patients. Also, the difference was accentuated in the supine position in healthy subjects, but not in glaucoma patients.4873
Comparing Goldmann and dynamic contour tonometry. Researchers at Moorfields Eye Hospital in London studied 130 eyes to compare IOP measurements made by Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) and Pascal dynamic contour tonometry (DCT). They found that both central corneal thickness and subject age affected GAT significantly more than DCT; differences between the two devices ranged up to 3 mmHg between the youngest and oldest eyes and between the thinnest and thickest corneas. Also, the relationship between GAT-measured IOP and CCT was significant; this wasn't the case for DCT. However, the DCT showed greater variability than the GAT.4838
Ocular characteristics' impact on IOP measurement. A study conducted at the Wilmer Eye Institute compared the influence of different ocular characteristics on IOP measurements made by three instruments: Goldmann applanation; the Tonopen; and the Reichert Non-Contact tonometer (NCT). The study involved 230 patients with glaucoma, ocular hypertension, or suspected glaucoma; IOP measurements were correlated to axial length, corneal curvature, corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis (a measure of bioelasticity).
The authors found that high average IOP was associated with a thicker cornea and steeper corneal curvature, but not axial length. They also found that the lowest and highest hysteresis values were associated with higher IOP values than mid-range hysteresis. Overall, Goldmann tonometry was least affected by corneal thickness, the NCT was least affected by corneal curvature, and the Tonopen was least affected by hysteresis.4868
Diurnal IOP shifts, upright and supine. A prospective clinical trial at the University of Dresden in Germany evaluated IOP in 30 glaucoma patients and 50 healthy controls every four hours, day and night, using Goldmann and Perkins tonometers (the former in upright position, the latter in both upright and supine positions).
Perkins tonometry produced IOP readings about 1 mmHg lower than Goldmann at noon, 8 p.m. and midnight in both groups. Perhaps more significantly, diurnal IOP change was similar in both groups when measured upright, and increased in both groups when supine—but the difference was greater in glaucoma patients. The authors hypothesize that this might indicate faulty regulation of fluid shift in glaucoma patients.4832
Blood Flow
Blood flow and visual stimuli: glaucoma patients vs. normals. A study conducted in Montreal has found that glaucoma patients show a significantly smaller increase in optic nerve head blood flow than healthy individuals in response to flicker stimulation. Nine normals and 11 glaucoma patients being treated with topical hypotensive therapy were monitored with a laser Doppler flowmetry instrument to detect blood flow changes on the superior-temporal neuroretinal rim, while researchers presented a green light flickering at 16 Hz. Blood flow in normal subjects increased 64 percent; blood flow in treated glaucoma patients only increased 7 percent. The study authors believe this indicates that some underlying vascular disturbances remain unchanged despite IOP-lowering treatment.5731
Glaucomatous ocular hemodynamics: African Americans vs. Caucasians. Researchers at Indiana University, the University of Cologne in Germany, and the Jules Stein Eye Institute in Los Angeles performed a retrospective analysis of six open-angle glaucoma studies, comparing color doppler imaging of the ophthalmic artery in a single eye of 62 African-American and 121 Caucasian glaucoma patients. They reviewed peak systolic velocity, end diastolic velocity, resistive index and IOP.
Caucasians' mean peak systolic velocity was 30.90 ±8.21 cm/s; African Americans' was significantly lower: 26.51 ±6.19 cm/s. Similarly, Caucasians' end diastolic velocity was 8.17 ±2.90, while African Americans' was 6.92 ±1.99. (No difference was found in mean resistive index or IOP.) The authors note that this kind of blood-flow difference might help explain why glaucoma is more prevalent in the African-American population.1330
VEP
Assessing a new instrument for detecting glaucomatous damage. A multicenter study conducted in the New York City area tested the efficacy of a new noninvasive visual evoked potential device. The instrument detects dysfunction in the "on" and "off" divisions of the magnocellular pathway that previous studies have shown to be related to glaucoma.
Data were collected from 23 participants with visual acuities of at least 20/30: 12 with open-angle glaucoma, three glaucoma suspects, two ocular hypertensives, and six age-similar controls. Ten-percent contrast stimulation revealed neural deficits in 11 of the 14 glaucomatous eyes with 20/20 visual acuity. Preliminary analysis of the data yielded accuracy estimates ranging from 79 percent to 96 percent, consistent with results achieved using earlier, more labor-intensive techniques.3758
ONH photography: film vs. digital. A study conducted at the New Jersey Medical School and West Virginia University compared glaucoma specialists' assessment of traditional simultaneous stereo photographs of optic nerves with their assessment of corresponding digital images. Pictures were obtained using a Nidek 3-DX stereo disc camera with standard 35-mm film and a new 6.1 megapixel digital camera. Digital images were evaluated directly from a computer monitor; digital and film images were presented at the same viewing size and luminance.
|
|
| A study found no significant differences in optic nerve head evaluation or image quality between traditional simultaneous stereo photographs and digital images presented on a computer monitor. The latter has several practical advantages. |
Comparing GDx VCC, HRT I, and stereo photographs. In a study conducted at the Rotterdam Eye Hospital in the Netherlands, one eye each of 40 healthy subjects, 48 glaucoma patients, and six ocular hypertension patients was measured with scanning laser polarimetry and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Researchers also obtained simultaneous stereoscopic optic-disc photographs. The data were analyzed by four glaucoma specialists, four general ophthalmologists, four residents in ophthalmology, and four optometrists.
The SLP Nerve Fiber Indicator proved to be most accurate as a diagnostic tool, followed by CSLO's Bathija linear discriminant function. Notably, automated analysis of measurements with the GDx VCC and HRT I had a higher diagnostic accuracy than classification of stereoscopic optic-disc photographs by glaucoma specialists. The intra- and interobserver agreement for optic-disc analysis was only moderate to good.4809
Using baseline parameters to predict POAG. A multicenter study ancillary to the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study evaluated 865 eyes of 438 participants to determine whether baseline confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy parameters (Heidelberg Retina Tomograph) were associated with later development of POAG endpoints.
Several baseline topographic optic-disc measurements alone, or combined with clinical and demographic factors, were significantly associated with the development of POAG, including larger cup-to-disc area ratio, cup depth, height contour, cup volume, reference-plane height, smaller rim area, ratio of rim area to disc area, and rim volume. In addition, classification as "outside normal limits" by the HRT and the Moorfields Regression Analysis were significantly associated with the development of POAG. The predictive value ranged from 14 percent for HRT classification and MRA (overall), to 40 percent for MRA (temporal superior).3631
Assessing early glaucoma using RNFL asymmetry. A University of Southern California study evaluated 687 normals and 37 patients with early glaucomatous damage for degree of asymmetry in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness between the right and left eyes. Subjects underwent a complete visual examination, including Stratus OCT scans of the peripapillary RNFL.
In normals the mean RNFL asymmetry was 4.5 ±3.7 µm, but patients with early glaucoma had a mean overall RNFL asymmetry of 6.4 ±6.9 µm, a significant difference. Although there were no consistent associations between RNFL asymmetry and age, gender, axial length, or spherical equivalent refractive error, the asymmetry in the superior RNFL was 48 percent greater in early glaucomatous patients than in normal subjects. The study authors conclude that asymmetry in the Stratus OCT-measured RNFL may be an early sign of glaucomatous optic-nerve damage.2521
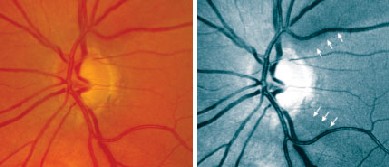
Pseudo red-free images vs. full color and conventional red-free. A randomized, masked study conducted at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine evaluated a new software program that converts color optic disc photographs into pseudo red-free images (forced RF) by removing the red-channel information and halving the intensity of the blue channel, to see whether this inexpensive approach could aid detection of nerve fiber bundle defects.
|
|
| A new software program converts color optic disc photographs into pseudo red-free images by removing the red-channel information and halving the intensity of the blue. |
Anterior segment OCT vs. gonioscopy. A multicenter study in Singapore and the United States is evaluating the anterior segment optical coherence tomograph (Carl Zeiss Meditec) to see how well it detects occludable angles. (The AS-OCT provides rapid, noncontact imaging of the drainage angle.) Patients at the National University Hospital in Singapore are undergoing imaging with the AS-OCT and gonioscopy using the Goldmann two-mirror lens.
Preliminary data from 54 eyes (29 patients) shows that the AS-OCT detected narrow or closed angles in temporal quadrants in 24 out of 28 rated occludable by gonioscopy (85.7 percent); 40 out of 46 inferior angles (87 percent); and 17 (89.5 percent) out of 19 nasal quadrants. Overall, the AS-OCT correctly identified 81 out of 93 occludable angle quadrants (87.1 percent) as narrow or closed.145
Glaucoma Surgery
Use of nonpenetrating surgery: survey results. An e-mail survey of members of the American Glaucoma Society regarding their use of viscocanalostomy and/or nonpenetrating deep sclerectomy (NDS) found that, in general, most of the surveyed surgeons prefer trabeculectomy. Sixteen percent of the respondents perform NDS, but only in cases of early glaucoma; the number of NDS procedures performed per year ranged from two to 150. Seven of the 82 respondents said they have performed NDS in the past, but stopped because they were not impressed by the resulting IOP reduction, the limited indications for these procedures, the unpredictable failures that occurred, or the need for repeated laser goniopuncture postoperatively.104
Comparing deep sclerectomy and trabeculectomy. A seven-year prospective, randomized, investigator-masked clinical trial at the University of Parma and University of Brescia in Italy compared the long-term outcomes of trabeculectomy and deep sclerectomy in 79 eyes of 79 patients. Sixty-two percent of the 41 patients randomized to deep sclerectomy also received YAG-laser goniopuncture during follow-up. Trabeculectomy controlled IOP better than deep sclerectomy seven years after surgery, but deep sclerectomy's success rate increased significantly when it was converted to a penetrating procedure using postoperative YAG-laser goniopuncture. Also, deep sclerectomy was associated with a lower incidence of cataract extraction.1217
CCT's impact on SLT. A retrospective chart review of all selective laser trabeculoplasty procedures performed at the University Eye Clinic in Dallas (53 patients/81 eyes) found that patients with thin corneas generally showed a greater reduction in IOP. Researchers noted, however, that when the patients were divided into three groups by corneal thickness, the trend was only statistically significant when comparing those in the thickest cornea group with those in the thinnest group.107
Outcomes with the ExPress miniature glaucoma shunt. Researchers at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center implanted the ExPress miniature glaucoma implant under a partial-thickness scleral flap with Mitomycin C in 52 eyes of 50 patients who were candidates for trabeculectomy, to study the procedure's complication rate and efficacy in lowering IOP. Fifteen of the eyes also underwent cataract surgery and IOL implantation.
At six months, IOP dropped from a preop baseline of 26.3 ±10.4 mmHg to 11.2 ±3.8, and 95.8 percent of eyes had an IOP between 4 and 22 mmHg. The mean number of medications was reduced to 0.4 ±1.0 at last follow-up. Three eyes (5.8 percent) developed choroidal detachments that resolved spontaneously. The authors conclude that this procedure is a safe and effective alternative to trabeculectomy.71
Comparing one- and two-site phacotrabeculectomy. A prospective, randomized, two-year clinical trial involving 80 patients at the University of Toronto is comparing the effectiveness of one- and two-site phacotrabeculectomy. Preliminary results have found no statistical difference in IOP between the two groups at three, six and 12 months of follow-up, or in the number of glaucoma medications in use (which decreased from a mean of 2.9 to zero for the one-site group, and from 2.9 to 0.1 for the two-site group). Researchers also failed to find any statistical difference in visual acuity improvement, but noted a trend to lower IOP in the two-site group.105
Long-term impact of 5-FU. Researchers in Singapore and London conducted a six-year, multicenter, prospective, randomized, masked trial to evaluate the long-term effect of a five-minute application of 5-Fluorouracil (50 mg/ml) during trabeculectomy on Asian patients. One hundred fifteen patients received 5-FU; 120 received placebo. The long-term data showed no significant differences in complications between groups, but a significant difference in successful outcomes, defined in terms of IOP. With a mean follow-up of 54 ±15.1 months, 83/115 of the 5-FU subjects exceeded 14 mmHg, compared with 101/120 in the placebo group; 57/115 of the 5-FU subjects exceeded 17 mmHg, compared with 73/120 of the placebo group.1219
Resolving encapsulated filtering blebs. Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the University of Texas conducted a retrospective case study of 39 eyes that had developed an encapsulated bleb following trabeculectomy, to determine how well different treatments aided resolution. Subjects were POAG patients with no prior history of neovascular or uveitic glaucoma, bleb revision or combined surgical procedures.
Of the 39 eyes, encapsulation was resolved with medical management in 29 (74.4 percent). In 20 of those eyes, Pred Forte was tapered (11 with multi-drug therapy; nine with Pred Forte taper alone). The authors conclude that bleb encapsulation following trabeculectomy responds well to tapering topical corticosteroids, alone or in conjunction with IOP-lowering agents. They also note that lowering IOP through steroid withdrawal appears to be more beneficial than maintaining steroid use to prevent inflammation.3779
Evaluating a novel glaucoma surgery. A study conducted at the State University of New York at Binghamton evaluated a new method of shunting aqueous into the suprachoroidal space as a way of lowering IOP. Fifty-six glaucomatous eyes received an internal tube silicone shunt, 15 shunting directly from the anterior chamber, 41 shunting from a deep scleral lake. At baseline, the mean IOP value in the anterior-chamber shunted eyes was 33.2 ±9.8 mmHg, on 3.4 meds; after 6.1 ±3.2 months it was 13.6 ±5.1 mmHg, on 1.7 meds. Also, IOP after a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor was 11.2 ±4.1 mmHg; after timolol, 11.3 ±4.2 mmHg.
|
|
| A new surgical treatment that shunts aqueous from the anterior chamber into the suprachoroidal space appears to be an effective way to lower IOP. |
Dr. Netland is the Siegal Professor, director of glaucoma and vice chair for academic affairs in the Department of Ophthalmology at the Hamilton Eye Institute, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tenn. Dr. Singh is professor of ophthalmology and director of the Glaucoma Service at Stanford University School of Medicine.
*Reference numbers noted as footnotes correspond to the abstract numbers in the 2005 ARVO program.