The growing belief that cataract patients are no longer satisfied with simply replacing their lens and providing "adequate" vision finds support in this year's ARVO abstracts. Which technologies and techniques will emerge to meet those demands is far from settled, but the studies show that refractive cataract surgery, blue-light blocking, accommodating lenses and other areas of interest and debate are alive and well.
Two-year data on Calhoun Vision's Light Adjustable Lens is offered by surgeons participating in the lens's trials. They're following 16 cataract patients implanted with the foldable, silicone LAL after standard phacoemulsification. At seven to 14 days postop, they assess BCVA, auto-refraction and contrast sensitivity. Using a digital light delivery device (Carl Zeiss Meditec), the surgeon adjusts the lens's power to achieve a pre-determined spherical and/or astigmatic change, and the same measures are repeated the following day. They report successful adjustment of spherical refractive error in eight consecutive patients from +1.5 D to -1.25 D. All of the achieved power changes were within 0.25 D of the attempted values, save one patient (within 0.5 D). Additional patients were successfully adjusted for postop astigmatic error. All patients maintained pre-adjustment BCVA and contrast sensitivity. No eyes showed any evidence of inflammation. The adjustment procedure was well-tolerated by all patients without complications.803
 |
 |
 |
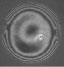
| A +20-D Light Adjustable Lens (left). The same LAL with a -1.5-D power adjustment (center), and then a +2-D central reading add (right). |
Investigators in New York City report, however, that posterior capsule opacification with the Crystalens appears to develop earlier and at a higher rate than with traditional IOLs. They reviewed the charts of 27 consecutive eyes of 25 Crystalens patients. A standardized surgical protocol was followed by a single surgeon using phacoemulsification with capsulorhexis (5 mm) and a scleral tunnel incision. Follow-up time ranged from one week to 10 months. They found that 44 percent (12/27) of patients developed slit-lamp evidence of PCO at a mean postop follow-up of 4.9 months. Only three of the 27 patients (11 percent) required a YAG capsulotomy for visually significant PCO at five months postop. One meta-analysis (Schaumberg, DA et al, Ophthalmology 105:1213-1221) reported pooled rates of PCO with traditional IOLs were 11.8 percent at one year, 20.7 percent at three years, and 28.4 percent at five years after surgery.2857
|
|
| Crystalens accommodates, but PCO rates were a concern in one study. |
An aspheric IOL design might decrease the influence of optic dislocation on higher-order aberrations, say investigators at Germany's Frankfurt University. They compared the influence of IOL tilt and decentration on total higher-order aberrations, spherical-like aberration and coma-like aberration between spheric and aspheric foldable IOLs.
Eighteen cataract patients received a spheric IOL (AMO AR40e) in one eye and an aspheric IOL (Pfizer Tecnis Z9000) in the fellow eye. Three months postop, ocular wavefront aberrations were measured using a Hartmann-Shack aberrometer. IOL tilt and decentration were evaluated with Scheimpflug photography.
Mean optic tilt was 2.89 ±1.46° for the spheric IOL and 2.85 ±1.36° for the aspheric IOL. Optic decentration measured 0.19 ±0.12 mm for the spheric IOL and 0.27 ±0.16 for the aspheric IOL. The spheric IOL showed a significant correlation between optic decentration and spherical-like aberration. Correlations between IOL tilt and decentration and total HOA or coma-like aberration were not significant. The aspheric IOL showed no significant correlations between IOL tilt or decentration and total HOA, spherical-like, or coma-like aberrations.811
IOL Blues
A blue light-absorbing IOL prevents retinal light damage more effectively than an ultraviolet-absorbing IOL, says a group at Japan's Showa University, Tokyo.
Thirty-one cataract patients there were randomly implanted with either a blue light-absorbing IOL (ENV-13, Menicon, Group 1: n=16, age 71.1 ±6.7) or ultraviolet-absorbing IOL (ES-13, Menicon, Group 2: n=15, age 71.2 ±6.6). At three and 12 months, the researchers measured the mean fluorescein transmittance by vitreous fluorophotometry, cystoid macular edema by fluorescence angiography, and the thickness of the fovea by OCT.808
|
Group 1 (Blue light) |
Mean fluorescein |
CME |
Foveal Thickness |
|
Three months |
2.83 ng/mL |
25 percent |
178.5 mm |
|
Group 2 (UV light) |
Mean fluorescein |
CME |
Foveal Thickness |
|
Three months |
3.02 ng/mL |
28 percent |
172.3mm |
An Alcon-affiliated researcher at the University of Texas Southwestern, in Dallas, conducted a meta-analysis of FDA clinical study results and published articles between 1990 and late 2004 comparing a blue-light filtering IOL to a UV-filtering IOL using visual acuity, color vision, contrast sensitivity, contrast enhancement, and quality of life tools as surrogates. He finds that blue light-filtering IOL technology provides equal or better visual performance under photopic and mesopic lighting conditions for patients after cataract surgery.
One year postop, 75.6 percent of blue light-filtering IOL clinical trial subjects achieved BCVA of 20/20 or better compared to 74 percent for control UV-only filtering IOL subjects. FDA clinical trials measures produced no statistical difference in implanted patient color vision for a blue light-filtering IOL vs. a UV-filtering IOL. Contrast sensitivity at 120 to 180 days after second eye implantation under photopic and mesopic lighting conditions found no statistical difference at three, six, 12, and 18 cycles per degree (cpd) between blue light- and UV-filtering IOL patients based on FDA study data. Other peer-reviewed research found significantly higher contrast sensitivities among blue light-filtering IOL patient groups at frequencies of 1.5, 3, and 6 cpd, vs. UV-filtering IOL patient groups under mesopic light conditions. Laboratory studies of blue light- vs. UV-filtering IOLs showed a 47 percent (red), 21 percent (green), and 21 percent (blue) contrast enhancement increase due to reduced chromatic aberration. QOL studies found bilaterally implanted blue light- and UV-filtering IOL patient comparisons comparable with a mean 99.4 vs. 98.6 percent rating for color vision, respectively, and a mean 91.2 vs. 90 percent rating for driving, respectively. (Scale ratings of 0-100. Higher scores equal more favorable vision-targeted QOL).807
In contrast, an AMO-supported study at the University of Alabama and Utah's Moran Eye Center suggests that blocking blue light leads to measurable impairments in scotopic sensitivity, and IOLs that do so may impair night vision.
In trial lenses they replicated the transmission curves of a 20 D Alcon AcrySof Natural blue-blocking IOL (trial lens) and a UV-blocking IOL (control lens) and twice measured scotopic sensitivity in eight pseudophakic, normal subjects (mean age 72) and three pseudophakic, mild AMD patients (mean age 76) at multiple wavelengths to determine whether tinted IOLs reduce scotopic sensitivity relative to UV-blocking IOLs. Each patient's scotopic visual field was measured once with each trial lens. The order of the trial lenses was counterbalanced across subjects. After 40 minutes of dark adaptation, scotopic sensitivity was measured at 410 nm, 450 nm, 500 nm, and 560 nm wavelengths using a modified Humphrey Field Analyzer. The stimulus was a 1.8-degree diameter circular test spot. Test locations were at 7 degrees eccentricity on each visual axis with an additional point at 18 degrees in the peripheral nasal field for the AMD subjects.
The mean impairment for the trial lens compared to the control lens for the normal group was 65 percent at 410 nm, 27 percent at 450 nm, 2 percent at 500 nm, and 4 percent at 560 nm. The AMD group was 55 percent at 410 nm, 44 percent at 450 nm, 4 percent at 500 nm, and 2 percent at 560 nm. Impairment was greater peripherally in the AMD group; 66 percent at 410 nm, 54 percent at 450 nm, 26 percent at 500 nm, and 21 percent at 560 nm.
The researchers are proceeding with a randomized, prospective study of scotopic vision in individuals implanted with the Alcon Natural IOL.806
Into the breach between these positions steps a group from Cornell, Columbia and New York University with an NIH-supported study in which they measured hue discrimination and dark-adapted sensitivity to a range of wavelengths in healthy young individuals.
Eighteen subjects, age 22 to 27, with corrected visual acuity of >20/20 were tested monocularly with and without a trial lens made with the same chromophore as the AcrySof Natural. This lens mimics the SN60AT transmission curve. Hue discrimination was measured with the FM 100-hue test under standard illuminant C conditions. Following pupil dilation and 40 minutes of dark adaptation, they measured rod-mediated thresholds to 440-nm, 500-nm, 650-nm and "white" light stimuli in 23 locations using a modified Humphrey perimeter. They found no changes in FM 100-hue error scores or axes with the lens. Dark-adapted sensitivities to the 440-nm stimulus were decreased by an average of 0.25 log unit with the lens. However, sensitivities to the 500-nm, 650-nm, and "white" light stimuli were only decreased by an average of 0.1 log unit, or what they call a "trivial" effect. The group concludes that the lens did not affect hue discrimination even under illuminant C conditions. Their verdict: Visual performance should not be significantly impaired.805
Surgical Issues
United Kingdom researchers found limited success with intracameral dilatation in cataract patients. Thirty-two consecutive eyes undergoing phacoemulsification cataract surgery had one drop of phenylephrine 2.5 percent instilled twice in the 30 minutes before surgery. Dilatation was completed with 0.3-ml lignocaine hydrochloride 1% injected intracamerally. Pupil size was measured immediately prior to surgery, at maximal dilatation and at the end of the operation. The surgeon scored the adequacy of pupil dilatation for surgery. For comparison, 10 patients' pupils were dilated at preoperative assessment with the standard dilatation regimen of 4 drops each of 1% cyclopentolate and 2.5% phenylephrine.
The mean maximal dilation was 7.6 mm and the mean surgical satisfaction score was 7/10. Maximal pupil dilatation was maintained until the end of surgery in 91 percent of eyes. Pupil constriction of 2 mm or more was seen in 9 percent of eyes. Poor pupil tone was noted in 10 percent of eyes. The mean pupil dilatation of the 10 pupils dilated at preop assessment with the standard regimen was 8 mm.
On the plus side, the researchers cited the potential reduction in corneal epithelial drop toxicity and improved convenience, with a caveat that maximal pupil diameter tended to be 0.5 mm smaller than with standard dilatation. There were reservations, however, about implementing its general use: Pupil size appeared less stable with intracameral dilatation, with a tendency for the pupil to constrict during the procedure in some cases, particularly brown eyes.749
A group at Northwestern University, in Chicago, focused its attention in this regard on IOL inserters. They identified a small subset of patients following clear corneal phacoemulsification cataract extraction that develop a thin sheet-like layer of tissue on the anterior surface of the IOL, distinct from the lens capsule. Theorizing that the material may be surface epithelial cells introduced into the eye by an IOL inserter, they prospectively studied 50 consecutive phacoemulsification cataract surgeries from a single cataract surgeon to determine if a relationship exists between the number of cells recovered and the incision site and size, inserter tip design, and IOL design.
The surgeon used either an empty AMO or Alcon Labs IOL inserter tip placed through the surgical incision, followed by a second inserter tip with the folded IOL that was then inserted into the capsular bag as routinely done. The tips were sent for analysis. Material from the interior was thoroughly scraped onto slides, fixed and stained. When present, epithelial cells were counted for each specimen. Scanning electron microscopy was performed on the inserter tips and/or IOLs that had been partially inserted in the eye and then removed.
Epithelial cells were found in more than 90 percent of the empty inserter tips with clear corneal incisions and more than 78 percent of the second tips inserted. Scleral tunnel incision often resulted in fewer samples with epithelial cells. The observed coating of the leading edge of the IOL optic after lens implantation has been shown to be epithelial cells. They recommend that debris injected with the IOL implantation should be aspirated from the eye following insertion.778
Various protective agents can be used as alternatives to BSS during routine cataract surgery and show significant improvement in corneal clarity and reduction of frequency of application during surgery, says a retrospective review of medical charts and surgical videos of patients at the University of Washington medical center. The subjects underwent routine cataract surgery during 2003-2004, and various corneal protective agents (Refresh Liquigel, Ocucoat, Provisc, Goniosol, Celluvisc and Tearasol) were used on the corneal surface instead of BSS during routine cataract surgery. Corneal clarity, the frequency and duration of required applications, total volume of agent used, the requirement of an assistant during the surgical procedure and postop corneal epithelium appearance were recorded.
The mean duration of application in the group studied ranged from one minute (BSS) to 19 minutes (for Provisc). Mean frequency of application ranged from 20 (BSS) per case to 1.1 (for Provisc). There was measurable difference in corneal clarity between the groups, and the majority of intraocular viscoelastics showed superior corneal clarity during the surgery.
The use of alternative corneal protective agents may provide an effective option in reducing the distraction to the patient and to the surgeon during surgery. The increased duration of application and improved clarity may obviate the need for a second assistant during a routine cataract surgery.785
Astigmatism Management
Contemporary small incisions for phacoemulsification are thought to be astigmatically neutral. Small scleral incisions may have less effect on changing the major axis of corneal curvature than small corneal incisions, says a pair of researchers at Columbia University's Harkness Eye Institute. They retrospectively studied 1,123 eyes operated for cataract by a single surgeon. The incisions reviewed include extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE), a 6-mm superior scleral tunnel (6Sup), a 3-mm superior scleral tunnel (3Sup), a 3-mm temporal scleral tunnel (3Temp), a 3.5-mm temporal corneal incision (3Cor), and a 2.6-mm corneal incision (2.6Cor). Corneal keratometry readings before and after surgery were divided into: spherical, steeper axis vertical, steeper axis oblique, and steeper axis horizontal. The pair compared the preop major axis of corneal curvature to the final major axis of corneal curvature during the first two years after surgery and determined the proportion of patients whose final axis differed from the preop axis by type of incision.
The proportion of patients whose final major axis of corneal curvature was significantly different from the preoperative major axis: ECCE (72 percent); 6Sup (47 percent); and 3Sup (38 percent). All of the superior incisions were more likely to change the major axis of corneal curvature than any of the temporal incisions. No significant difference in changed axis was detected between the 3.5- (28 percent) and 2.6-mm (30 percent) corneal incisions. However, both corneal incisions were slightly but significantly more likely to change the major axis of corneal curvature than the 3-mm temporal scleral tunnel incision (28 percent vs. 15 percent).775
Three-day preoperative antibiotic therapy was more effective in reducing bacterial flora than one-day in patients undergoing cataract surgery, according to an Allergan-supported study.
The prospective clinical trial evenly randomized 50 patients to receive gatifloxacin 0.3 percent (Zymar, Allergan) in the eye to receive surgery one hour prior to surgery as well as a standard 5% povidone iodine surgical prep. The study group (n=25) received additional gatifloxacin 0.3 percent therapy for three days prior to surgery, and were considered to be in the study group. The 25 patients who did not receive the three-day dosing regimen were the control group.
In cultures taken immediately before cataract surgery, eight of 25 (32 percent) of the controls (one-hour) had positive conjunctival cultures vs. five of 25 (20 percent) in the study (three-day) group. Immediately following surgery, five of 25 controls (20 percent) had positive cultures vs. three of 25 (12 percent) in the study group.794
Researchers affiliated with ISTA Pharmaceuticals at various locations report the Phase-III randomized, placebo-controlled studies of the company's bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.1 percent (Xibrom). The NSAID received marketing approval last month.
 |
| ISTA Pharmaceutical's Xibrom was recently approved as a b.i.d. NSAID. |
Intravitreal Kenalog at the time of cataract extraction improves visual acuity and can decrease macular thickness in eyes with preoperative clinically significant diabetic macular edema and diffuse macular leakage, based on a seven-case retrospective analysis at California's Loma Linda University.
In the seven cases of CSDME, pars plana intravitreal Kenalog injections were performed intraoperatively at the time of cataract surgery over a 17-month period. Indications were the presence of a visually significant cataract, difficulty with treating the macular edema due to cataract, and the presence of diffuse macular leakage on preop fluorescein angiography.
VA improved in each case by the time of their final exam with a mean follow-up time of 5.3 months. Preop VA ranged from count fingers at one foot to 20/400 and improved to CF at six feet to 20/30-2 postoperatively. Five of the seven eyes (71 percent) improved Ž2 lines; the remaining improved the equivalent of one line. OCT comparison of pre- and postop central macular thickness was done in three eyes; CMT improvement was noted in two, with mean decrease by 176.5 µm (54 percent). The CMT of the remaining eye increased from 347 to 469 µm (135 percent). One patient developed steroid induced glaucoma postoperatively, requiring medical therapy. No other adverse events were noted.783
A new electronic device paints a grim picture of compliance with medical therapy. Researchers in Germany and Turkey studied 20 cataract patients (mean age: 62.9 years) in what they call the first study to electronically monitor compliance in ambulant cataract patients. Subjects were asked to apply a fixed combination of prednisolone and gentamycin five times daily between 8 a.m. and 10 p.m. for 14 days postoperatively. Ten of the patients were randomly assigned to keep the bottles refrigerated. A microprocessor-controlled compliance device monitored date, time and ambient temperature of each application.
All patients were non-compliant with regards to total dose, time intervals or premature discontinuation of therapy. The mean of total administered drops was 33.3 ±15.7 drops per patient for the observed 14 day period; range: 10-74. The prescribed total dose was 70 drops per eye. As determined by the monitor 10 patients took less than one-half, four less than one-quarter of the prescribed medication. The rate of compliance was not higher in the last 24 hours preceding the return appointment. Recorded temperatures of the group assigned to keep the bottles refrigerated were significantly lower compared to the other participants.
The new device presents a basis for studying compliance with topical ocular therapy.3832
Can an NSAID-impregnated IOL make postop meds for inflammation control unnecessary? Researchers in France say yes. Their prospective, randomized study enrolled 34 cataract patients randomly assigned to receive diclofenac-impregnated IOL (Group A) or control IOL and topical treatment with sodium diclofenac 0.1 percent (1 drop, t.i.d. for four weeks, Group B).
AC inflammation was measured with a laser flare meter preoperatively and one, seven, 21, 30 and 90 days postop. OCT was performed preop and 30 days postop to detect cystoid macular edema. Clinical signs of inflammation and tolerance and best-corrected visual acuity were also registered.
No statistical significant difference with regard to flare evolution was found between the groups, and the difference of flare measurement between each evaluation time and baseline was always similar between groups. The variation of macular thickness evaluated by OCT was similar, as well. Postop BCVA represented a gain of 4 to 5 lines in both groups compared with preop. Clinical signs of inflammation and tolerance were similarly distributed between groups.786
Endophthalmitis Rising?
The rate of endophthalmitis following cataract surgery in the United States has been increasing based on Medicare data, though the data does not provide an explanation.
A group from Johns Hopkins University sampled Medicare beneficiary data files for inpatient and outpatient claims from 1994 through 2001 and identified all cataract surgeries and subsequent cases of endophthalmitis following cataract surgery based on claims submitted. They tallied 1,079 cases of presumed endophthalmitis following 502,357 cataract surgeries, an incidence rate of 2.15/1,000 for this eight-year period.
Age-gender-race adjusted rates of endophthalmitis were significantly higher in 1998 to 2001 compared to earlier years (risk ratio: 1.39). Older age (risk ratio: 1.89) and black race (risk ratio: 1.42) also were associated with increased risk of endophthalmitis.
An increase in endophthalmitis rates following the nation's most commonly performed operation is of concern, particularly as the numbers will likely increase over the coming decades due to the aging of the U.S. population.5567
Canada, too, is experiencing increased cataract surgery-related endophthalmitis, say investigators at Dalhousie University. They retrospectively analyzed 17,438 cataract surgeries with PCIOL implantation at the Victoria General Hospital, Halifax, 1999 to 2003. There, 36 patients developed endophthalmitis (0.206 percent).
Temporal incision was used in 33 cases (92 percent) and a clear cornea approach in 33 cases (92 percent). A nonfoldable lens was used in 22 cases (61 percent). Fourteen (39 percent) received intraoperative vancomycin. Vitreous was sent for cultures in all 36 cases (100 percent), with 33 (92 percent) yielding positive results.
Anterior-chamber fluid was sent for cultures in 14 cases (39 percent), and yielded positive results in four cases (11 percent), though two of these showed negative vitreous culture results. Vitreous cultures yielded positive results in 33 cases (92 percent). Coagulase-negative staphylococcus was the most common agent identified (58 percent).
The group says that factors leading to a higher incidence of postop endophthalmitis than described in previous studies may include nonfoldable lenses, temporal incisions and clear cornea approach. An anterior chamber aspirate may yield positive culture results when vitreous cultures are negative. The responsible organisms causing endophthalmitis showed increasing trends towards antibiotic resistance, particularly tobramycin.5570
Dr. Blecher, Review's chief medical editor, is co-director of the Cataract Department at the Wills Eye Hospital, in Philadelphia.
*Reference numbers noted as footnotes correspond to the abstract numbers in the 2005 ARVO program.




